# 三、运行时核心
本章内容图解
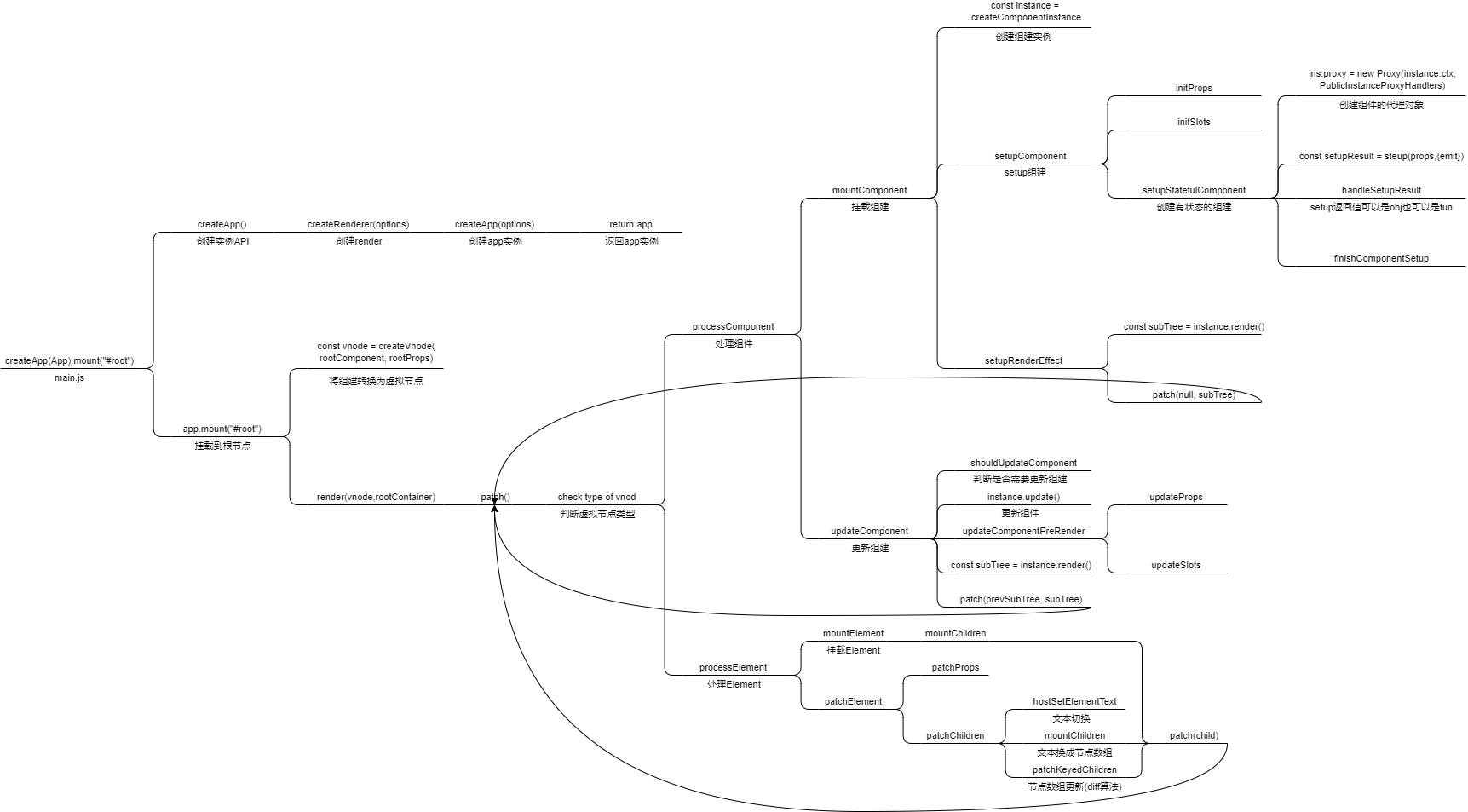
可以以这张图为向导, 阅读本章节
GitHub: https://github.com/Roman-29/mini-vue
# 初始化主流程
观察图片, 如果我们要实现功能, 可以将主流程分为 component 和 element 两个方向处理
# 测试代码
App.js
import { createVnode as h } from "../../lib/mini-vue.esm.js";
export const App = {
render() {
return h(
// type
"div",
// props
{
id: "root",
class: ["red", "hard"],
},
// children
[h("p", { class: "red" }, "hi"), h("p", { class: "blue" }, "mini-vue")]
);
},
setup() {
return {};
},
};
main.js
import { createApp } from "../../lib/mini-vue.esm.js";
import { App } from "./App.js";
const rootContainer = document.querySelector("#app");
createApp(App).mount(rootContainer);
index.html
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.red {
color: red;
}
.blue {
color: blue;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app"></div>
<script src="main.js" type="module"></script>
</body>
</html>
# component 主流程代码
创建 createApp.ts 作为整个运行时的起始
import { render } from "./renderer";
import { createVnode } from "./vnode";
export function createApp(rootComponent) {
return {
mount(rootContainer) {
// 将组件转化为虚拟节点
// component -> vnode
const vnode = createVnode(rootComponent);
render(vnode, rootContainer);
},
};
}
创建的 app 实例应该有个 mount 方法, 用于挂载节点. 对组件进行渲染时需要根据用途分类新建代码文件处理:
vnode.ts 用来转换虚拟节点
export function createVnode(type, props?, children?) {
const vnode = {
type,
props,
children,
el,
};
return vnode;
}
renderer.ts 用来渲染虚拟节点
import { createComponentInstance, setupComponent } from "./component";
export function render(vnode, container) {
patch(vnode, container);
}
function patch(vnode, container) {
// 处理组件
processComponent(vnode, container);
}
function processComponent(vnode, container) {
mountComponent(vnode, container);
}
function mountComponent(vnode, container) {
const instance = createComponentInstance(vnode);
setupComponent(instance);
setupRenderEffect(instance, container);
}
function setupRenderEffect(instance, container) {
const subTree = instance.render();
// 拿到组件render函数渲染的虚拟节点继续递归patch
patch(subTree, container);
initialVNode.el = subTree.el;
}
component.ts 用来处理组件内容
import { proxyRefs } from "../reactivity";
export function createComponentInstance(vnode) {
const component = {
vnode,
type: vnode.type, // 类型
setupState: {}, // setup的return值
el: null, // 组件对应的DOM节点
props: {},
slots: {},
};
return component;
}
export function setupComponent(instance) {
// TODO
// initProps
// initSlots
setupStatefulComponent(instance);
}
function setupStatefulComponent(instance) {
const Component = instance.type;
const { setup } = Component;
if (setup) {
const setupResult = setup();
handleSetupResult(instance, setupResult);
}
}
function handleSetupResult(instance, setupResult) {
// function or object
// TODO function(render函数)
if (typeof setupResult === "object") {
// 这里需要将setup里的ref对象全部代理出来, 从setupResult获取的ref都不再需要.value获取值
instance.setupState = proxyRefs(setupResult);
}
finishComponentSetup(instance);
}
function finishComponentSetup(instance) {
const Component = instance.type;
if (Component.render) {
instance.render = Component.render;
}
}
# element 主流程代码
renderer.ts 之前只处理了 component 类型的虚拟节点, 现在补充处理 element 节点
function patch(vnode, container) {
// 需要判断vnode是组件还是element
if (typeof vnode.type === "string") {
// type是
processElement(vnode, container);
} else if (isObject(vnode.type)) {
// 处理组件
processComponent(vnode, container);
}
}
function processElement(vnode, container) {
mountElement(vnode, container);
}
function mountElement(vnode, container) {
const el = (vnode.el = document.createElement(vnode.type));
const { props, children } = vnode;
for (const key in props) {
const val = props[key];
el.setAttribute(key, val);
}
if (typeof children === "string") {
el.textContent = children;
} else if (Array.isArray(children)) {
mountChildren(vnode, el);
}
container.append(el);
}
function mountChildren(vnode, container) {
vnode.children.forEach((v) => {
patch(v, container);
});
}
# 实现组价代理对象
# 简介
上面我们实现的组件渲染并没有将变量用到组件渲染中, 现在我们修改测试代码, 将 setup 中返回的变量放到 render 函数中
App.js
export const App = {
render() {
return h(
"div",
{
id: "root",
class: ["red", "hard"],
},
this.msg
);
},
setup() {
return {
msg: "power by mini-vue",
};
},
};
# 代码
要实现在 render 函数中使用 this 调用到 setup 的值, 就需要用到代理对象
在 component.ts 中创建 proxy
import { PublicInstanceProxyHandles } from "./componentPublicInstance";
function setupStatefulComponent(instance) {
const Component = instance.type;
// 执行setup之前先给组件创建代理对象
instance.proxy = new Proxy({ _: instance }, PublicInstanceProxyHandles);
const { setup } = Component;
if (setup) {
const setupResult = setup();
handleSetupResult(instance, setupResult);
}
}
componentPublicInstance.ts
// 代理出组件实例的关键信息
const publicPropertiesMap = {
$el: (i) => i.vnode.el,
$slots: (i) => i.slots,
$props: (i) => i.props,
};
export const PublicInstanceProxyHandles = {
get: function({ _: instance }, key) {
// setup属性
const { setupState } = instance;
if (hasOwn(setupState, key)) {
return setupState[key];
}
// 组件属性
const pulicGetter = publicPropertiesMap[key];
if (pulicGetter) {
return pulicGetter(instance);
}
},
};
const hasOwn = (val, key) => Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(val, key);
修改 renderer.ts
function setupRenderEffect(instance, initialVNode, container) {
const { proxy } = instance;
// render函数this指向proxy
const subTree = instance.render.call(proxy);
// vnode-> patch
// vnode-> element-> mountElement
patch(subTree, container);
initialVNode.el = subTree.el;
}
# shapeFlags
# 简介
shapeFlags 是描述虚拟节点的类型的一种标识, 用来更好的区分虚拟节点, 进行不同的逻辑处理.
# 代码
新建 ShapeFlags.ts 通过位运算判断类型
export const enum ShapeFlags {
ELEMENT = 1, // 0001
STATEFUL_COMPONENT = 1 << 1, // 0010
TEXT_CHILDREN = 1 << 2, // 0100
ARRAY_CHILDREN = 1 << 3, // 1000
}
修改 vnode.ts 将 ShapeFlags 挂载到虚拟节点上
import { ShapeFlags } from "../share/ShapeFlags";
export function createVnode(type, props?, children?) {
const vnode = {
type,
props,
children,
shapeFlag: getShapeFlag(type),
el: null,
};
if (typeof children === "string") {
vnode.shapeFlag |= ShapeFlags.TEXT_CHILDREN;
} else if (Array.isArray(children)) {
vnode.shapeFlag |= ShapeFlags.ARRAY_CHILDREN;
}
return vnode;
}
最后修改 renderer.ts
function patch(vnode, container) {
// 需要判断vnode是组件还是element
const { shapeFlag } = vnode;
if (shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.ELEMENT) {
processElement(vnode, container);
} else if (shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.STATEFUL_COMPONENT) {
// 处理组件
processComponent(vnode, container);
}
}
function mountElement(vnode, container) {
const el = (vnode.el = document.createElement(vnode.type));
const { props, children, shapeFlag } = vnode;
for (const key in props) {
const val = props[key];
el.setAttribute(key, val);
}
// 判断子节点类型
if (shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.TEXT_CHILDREN) {
el.textContent = children;
} else if (shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.ARRAY_CHILDREN) {
mountChildren(vnode, el);
}
container.append(el);
}
# 事件注册功能
# 简介
在 render 函数中的 props 参数增加一个事件名, 用来注册事件, 测试代码如下
export const App = {
render() {
return h(
"div",
{
id: "root",
class: ["red", "hard"],
onClick() {
console.log("click");
},
onMousedown() {
console.log("mousedown");
},
},
this.msg
);
},
setup() {
return {
msg: "power by mini-vue",
};
},
};
# 代码
修改 renderer.ts , 在挂载 element 的时候将事件注册到 el 中
function mountElement(vnode, container) {
const el = (vnode.el = document.createElement(vnode.type));
const { props, children, shapeFlag } = vnode;
for (const key in props) {
const val = props[key];
// 判断是否为事件
const isOn = (key: string) => /^on[A-Z]/.test(key);
if (isOn(key)) {
const event = key.slice(2).toLowerCase();
el.addEventListener(event, val);
} else {
el.setAttribute(key, val);
}
}
if (shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.TEXT_CHILDREN) {
el.textContent = children;
} else if (shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.ARRAY_CHILDREN) {
mountChildren(vnode, el);
}
container.append(el);
}
# 组件的 props 功能
# 简介
在父子组件通信的时候, 我们会用到 props 将父组件的数据传递给子组件, 测试代码如下:
App.js
export const App = {
render() {
return h(
"div",
{
id: "root",
},
[h(Foo, { count: 1 })]
);
},
setup() {
return {
msg: "power by mini-vue",
};
},
};
const Foo = {
name: "foo",
setup(props) {
console.log(props);
},
render() {
// this.count可以获取到值
return h("div", {}, "foo: " + this.count);
},
};
# 代码
修改 component.ts , 在 setup 的时候初始化 props
export function setupComponent(instance) {
// 初始化props, 将虚拟节点的props挂载到组件中
instance.props = instance.vnode.props || {};
// TODO
// initSlots
setupStatefulComponent(instance);
}
function setupStatefulComponent(instance) {
const Component = instance.type;
// 执行setup之前先给组件创建代理对象
instance.proxy = new Proxy({ _: instance }, PublicInstanceProxyHandles);
const { setup } = Component;
if (setup) {
// 对props进行shallowReadonly封装, 禁止子组件修改props
const setupResult = setup(shallowReadonly(instance.props));
handleSetupResult(instance, setupResult);
}
}
子组件如何通过 this 访问 props 呢? 也是通过代理, 在 componentPublicInstance 增加获取 props 的逻辑
export const PublicInstanceProxyHandles = {
get: function({ _: instance }, key) {
const { setupState, props } = instance;
if (key in setupState) {
return setupState[key];
}
if (hasOwn(setupState, key)) {
return setupState[key];
} else if (hasOwn(props, key)) {
// 如果key在props里有值, 就返回props的值
return props[key];
}
const pulicGetter = publicPropertiesMap[key];
if (pulicGetter) {
return pulicGetter(instance);
}
},
};
# 组件 emit 功能
# 简介
在父子组件通信的时候, 我们会用到 emit 在子组件触发自定义事件, 测试代码如下:
App.js
export const App = {
name: "App",
render() {
// emit
return h("div", {}, [
h("div", {}, "App"),
h(Foo, {
onAdd(a, b) {
console.log("onAdd", a, b);
},
}),
]);
},
setup() {
return {};
},
};
const Foo = {
name: "foo",
render() {
const btn = h(
"button",
{
onClick: this.emitAdd,
},
"emitAdd"
);
const foo = h("p", {}, "foo");
return h("div", {}, [foo, btn]);
},
setup(props, { emit }) {
const emitAdd = () => {
emit("add", 1, 2);
};
return {
emitAdd,
};
},
};
# 代码
修改 component.ts 将 emit 存放到组件实例中, 并且放到 setup 参数中
import { emit } from "./componentEmit";
export function createComponentInstance(vnode) {
const component = {
vnode,
type: vnode.type,
setupState: {},
el: null,
props: {},
slots: {},
emit: () => {},
};
// 锁定第一个参数是组件instance
component.emit = emit.bind(null, component) as any;
return component;
}
function setupStatefulComponent(instance) {
const Component = instance.type;
// 执行setup之前先给组件创建代理对象
instance.proxy = new Proxy({ _: instance }, PublicInstanceProxyHandles);
const { setup } = Component;
if (setup) {
// 对props进行shallowReadonly封装, 禁止子组件修改props
const setupResult = setup(shallowReadonly(instance.props), {
emit: instance.emit,
});
handleSetupResult(instance, setupResult);
}
}
新增 componentEmit.ts 专门处理 emit
export function emit(instance, event, ...args) {
// 父组件自定义事件也是存放在 props 中
const { props } = instance;
const handlerName = toHandlerKey(camelize(event));
const handler = props[handlerName];
handler && handler(...args);
}
// 增加on开头
const toHandlerKey = (str) => {
return str ? "on" + capitalize(str) : "";
};
// add -> Add
const capitalize = (str: string) => {
return str.charAt(0).toUpperCase() + str.slice(1);
};
// add-foo -> addFoo
const camelize = (str: string) => {
return str.replace(/-(\w)/g, (_, c: string) => {
return c ? c.toUpperCase() : "";
});
};
这样在调取 emit 的时候, 会将事件名进行重写, 并匹配执行 props 中对应的事件
# Fragment 和 Text 节点
# 简介
Fragment 和 Text 节点是新的虚拟节点类型
Fragment 类型不会创建父节点, 只渲染子节点
Text 类型是文本节点
# 代码
在 vnode.ts 新增这两个节点
export const Fragment = Symbol("Fragment");
export const Text = Symbol("Text");
在 renderer.ts 中, 当 patch 节点的时候判断类型
import { Fragment, Text } from "./vnode";
function patch(vnode, container) {
// 需要判断vnode是组件还是element
const { type, shapeFlag } = vnode;
switch (type) {
// Fragment只渲染children
case Fragment:
processFragment(vnode, container);
break;
case Text:
processText(vnode, container);
break;
default:
if (shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.ELEMENT) {
processElement(vnode, container);
} else if (shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.STATEFUL_COMPONENT) {
// 处理组件
processComponent(vnode, container);
}
break;
}
}
function processFragment(vnode, container) {
// 直接渲染子节点
mountChildren(vnode, container);
}
function processText(vnode, container) {
const { children } = vnode;
const textNode = (vnode.el = document.createTextNode(children));
container.append(textNode);
}
# 组件 slots 功能
# 简介
测试代码如下:
App.js
import { renderSlots } from "../../lib/mini-vue.esm.js";
export const App = {
name: "App",
render() {
const app = h("div", {}, "App");
const foo = h(
Foo,
{},
{
// 作用域插槽, age在子组件中
header: ({ age }) => h("p", {}, "header" + age),
footer: () => h("p", {}, "footer"),
}
);
return h("div", {}, [app, foo]);
},
setup() {
return {};
},
};
const Foo = {
setup() {
return {};
},
render() {
const foo = h("p", {}, "foo");
// 通过renderSlots把slots转换为vnode参与渲染
const age = 18;
return h("div", {}, [
renderSlots(this.$slots, "header", { age }),
foo,
renderSlots(this.$slots, "footer"),
]);
},
};
# 代码
首先在创建组件虚拟节点的时候, 预处理插槽, 修改 vnode.ts 和 ShapeFlags.ts
export function createVnode(type, props?, children?) {
const vnode = {
type,
props,
children,
shapeFlag: getShapeFlag(type),
el: null,
};
if (typeof children === "string") {
vnode.shapeFlag |= ShapeFlags.TEXT_CHILDREN;
} else if (Array.isArray(children)) {
vnode.shapeFlag |= ShapeFlags.ARRAY_CHILDREN;
}
// 判断虚拟节点是否为组件
if (vnode.shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.STATEFUL_COMPONENT) {
// 判断是否有 children 作为 slots
if (typeof children === "object") {
vnode.shapeFlag |= ShapeFlags.SLOT_CHILDREN;
}
}
return vnode;
}
export const enum ShapeFlags {
ELEMENT = 1, // 0001
STATEFUL_COMPONENT = 1 << 1, // 0010
TEXT_CHILDREN = 1 << 2, // 0100
ARRAY_CHILDREN = 1 << 3, // 1000
SLOT_CHILDREN = 1 << 4,
}
修改 component.ts 在 setup 的时候初始化 slots
export function setupComponent(instance) {
initProps(instance, instance.vnode.props);
// 组件虚拟节点的children就是组件的插槽
initSlots(instance, instance.vnode.children);
setupStatefulComponent(instance);
}
function initSlots(instance, children) {
const { vnode } = instance;
if (vnode.shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.SLOT_CHILDREN) {
normalizeObjectSlots(children, instance.slots);
}
}
// 具名插槽
function normalizeObjectSlots(children, slots) {
for (const key in children) {
const value = children[key];
// slot是一个函数, props是作用域插槽的参数
// 返回一个虚拟节点数组
slots[key] = (props) => normalizeSlotValue(value(props));
}
}
// slots需要是数组, 才能在后续被createVnode转换为虚拟节点
function normalizeSlotValue(value) {
return Array.isArray(value) ? value : [value];
}
新增 renderSlots.ts 用来渲染 slots
import { createVnode, Fragment } from "../vnode";
export function renderSlots(slots, name, props) {
const slot = slots[name];
if (slot) {
if (typeof slot === "function") {
// props是作用域插槽的参数
return createVnode(Fragment, {}, slot(props));
}
}
}
# getCurrentInstance 功能
# 简介
创建一个 API, 用来获取当前正在执行 setup 的组件实例对象
# 代码
修改 component.ts
function setupStatefulComponent(instance) {
const Component = instance.type;
instance.proxy = new Proxy({ _: instance }, PublicInstanceProxyHandles);
const { setup } = Component;
if (setup) {
// 设置当前组件实例
setCurrentInstance(instance);
const setupResult = setup(shallowReadonly(instance.props), {
emit: instance.emit,
});
setCurrentInstance(null);
handleSetupResult(instance, setupResult);
}
}
let currentInstance = null;
export function getCurrentInstance() {
return currentInstance;
}
export function setCurrentInstance(instance) {
currentInstance = instance;
}
# 组件 provides 和 inject 功能
# 简介
跨层级的组件存取数据
测试代码:
import { h, provide, inject } from "../../lib/mini-vue.esm.js";
export default {
name: "App",
setup() {},
render() {
return h("div", {}, [h("p", {}, "apiInject"), h(Provider)]);
},
};
const Provider = {
name: "Provider",
setup() {
provide("foo", "fooVal");
provide("bar", "barVal");
},
render() {
return h("div", {}, [h("p", {}, "Provider"), h(ProviderTwo)]);
},
};
const ProviderTwo = {
name: "ProviderTwo",
setup() {
provide("foo", "fooTwo");
const foo = inject("foo");
return {
foo,
};
},
render() {
return h("div", {}, [
h("p", {}, `ProviderTwo foo:${this.foo}`),
h(Consumer),
]);
},
};
const Consumer = {
name: "Consumer",
setup() {
const foo = inject("foo");
const bar = inject("bar");
const baz = inject("baz", () => "bazDefault");
return {
foo,
bar,
baz,
};
},
render() {
return h("div", {}, `Consumer: - ${this.foo} - ${this.bar} - ${this.baz}`);
},
};
# 代码
修改 component.ts , 在创建组件实例的时候需要传入组件的父节点, 这样就能将 provides 层层传递下去
export function createComponentInstance(vnode, parent) {
const component = {
vnode,
type: vnode.type,
setupState: {},
el: null,
props: {},
slots: {},
provides: parent ? parent.provides : {},
parent,
emit: () => {},
};
// 锁定第一个参数是组件instance
component.emit = emit.bind(null, component) as any;
return component;
}
新增 apiInject.ts , 处理 provide 和 inject
import { getCurrentInstance } from "./component";
export function provide(key: string, value: any) {
const currentInstance: any = getCurrentInstance();
if (currentInstance) {
// 获取当前组件的provides
let { provides } = currentInstance;
// 获取当前组件的父组件的provides
const parentProvides = currentInstance.parent.provides;
// 如果相同说明首次使用provide api, 进行初始化
if (provides === parentProvides) {
// 初始化当前组件的provides, 使用原型链保持对父组件的provides的关联
provides = currentInstance.provides = Object.create(parentProvides);
}
provides[key] = value;
}
}
export function inject(key, defaultValue) {
const currentInstance: any = getCurrentInstance();
if (currentInstance) {
const parentProvides = currentInstance.parent.provides;
if (key in parentProvides) {
return parentProvides[key];
} else {
if (typeof defaultValue === "function") {
return defaultValue();
}
return defaultValue;
}
}
}
provide 使用原型链的方式将属性一层一层传下去, 这样既能保障之间保持对父组件的 provides 的关联, 又不会出现多层之间属性被替换的问题
# 自定义渲染器
# 简介
在我们之前处理 element 的逻辑中, 都是默认渲染 DOM, 但是如果可以将渲染节点中的创建, 赋值, 挂载抽离出来, 便可以自定义一个渲染器, 用来渲染到其他平台.
# 代码
修改 renderer.ts , 不直接提供 render 函数, 而是将创建,赋值,插入等逻辑抽离成参数, 方便实现自定义渲染, 再向外提供.
import { createAppAPI } from "./createApp";
export function createRenderer(options) {
const {
createElement: hostCreateElement,
patchProp: hostPatchProp,
insert: hostInsert,
} = options;
function render(vnode, container) {
patch(vnode, container, null);
}
...
function mountElement(vnode, container, parentComponent) {
const el = (vnode.el = hostCreateElement(vnode.type));
const { props } = vnode;
for (const key in props) {
const val = props[key];
hostPatchProp(el, key, val);
}
const { children, shapeFlag } = vnode;
if (shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.TEXT_CHILDREN) {
el.textContent = children;
} else if (shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.ARRAY_CHILDREN) {
mountChildren(vnode, el, parentComponent);
}
hostInsert(el, container);
}
...
return {
createApp: createAppAPI(render),
};
}
原来的 render 函数不再向外提供, 那么在 createApp.ts 就需要将 render 做为参数引入
export function createAppAPI(render) {
return function createApp(rootComponent) {
return {
mount(rootContainer) {
// 将组建转化为虚拟节点
// component -> vnode
const vnode = createVnode(rootComponent);
render(vnode, rootContainer);
},
};
};
}
最后新增 runtime-dom/index.ts 将 DOM API 的代码放到这个地方, 作为默认的渲染器
import { createRenderer } from "../runtime-core";
function createElement(type) {
return document.createElement(type);
}
function patchProp(el, key, val) {
const isOn = (key: string) => /^on[A-Z]/.test(key);
if (isOn(key)) {
const event = key.slice(2).toLowerCase();
el.addEventListener(event, val);
} else {
el.setAttribute(key, val);
}
}
function insert(el, container) {
container.append(el);
}
// 使用 createRenderer API 创建render
const renderer: any = createRenderer({
createElement,
patchProp,
insert,
});
export function createApp(...args) {
return renderer.createApp(...args);
}
export * from "../runtime-core";
# 总结
经过以上的改造后, 当我们想往常使用 createApp 的时候, 会先创建一个默认的 renderer , renderer 包含一个 createApp 方法会把当前的 render 传入并使用
如果我们需要实现自己的渲染器, 参考代码如下:
import { createRenderer } from "../../lib/mini-vue.esm.js";
import { App } from "./App.js";
const game = new PIXI.Application({
width: 500,
height: 500,
});
// 创建画布
document.body.append(game.view);
// 自定义渲染器
const renderer = createRenderer({
createElement(type) {
if (type === "rect") {
const rect = new PIXI.Graphics();
rect.beginFill(0xff0000);
rect.drawRect(0, 0, 100, 100);
rect.endFill();
return rect;
}
},
patchProp(el, key, val) {
el[key] = val;
},
insert(el, parent) {
parent.addChild(el);
},
});
// 使用自定义渲染器创建App
renderer.createApp(App).mount(game.stage);