# 四、运行时更新
本章内容图解
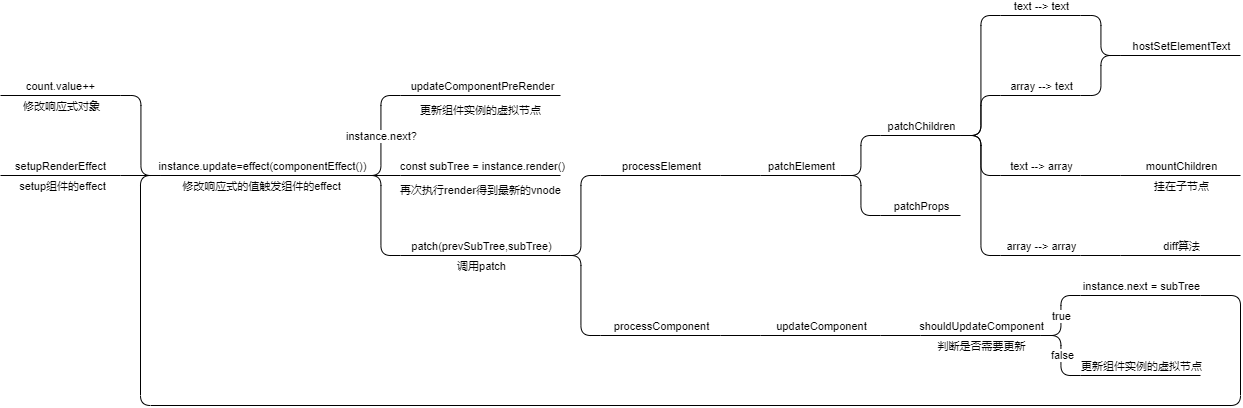
可以以这张图为向导, 阅读本章节
GitHub: https://github.com/Roman-29/mini-vue
# 更新 element 流程
# 简介
当组件的响应式对象发生改变的时候, 我们需要同步修改页面视图, 比如下面代码, 点击按钮后数字需要更新
import { h, ref } from "../../lib/mini-vue.esm.js";
export const App = {
name: "App",
setup() {
const count = ref(0);
const onClick = () => {
count.value++;
};
return {
count,
onClick,
};
},
render() {
return h(
"div",
{
id: "root",
},
[
h("div", {}, "count:" + this.count), // 依赖收集
h(
"button",
{
onClick: this.onClick,
},
"click"
),
]
);
},
};
# 代码
既然要更新, 就需要将更新前和更新后的虚拟节点做对比.
要拿到虚拟节点我们就要找到组件创建虚拟节点的地方 renderer.ts
要实现响应式更新, 就要用到前面实现的 effect 做依赖收集和调用
先修改 component.ts 增加三个属性到组件实例上
export function createComponentInstance(vnode, parent) {
const component = {
vnode,
type: vnode.type,
setupState: {},
el: null,
props: {},
slots: {},
provides: parent ? parent.provides : {},
parent,
isMounted: false, // 组件是否已挂载
subTree: {}, // 虚拟节点
next: null, // 更新后的虚拟节点
emit: () => {},
};
// 锁定第一个参数是组件instance
component.emit = emit.bind(null, component) as any;
return component;
}
再修改 renderer.ts
import { effect } from "../reactivity/effect";
export function createRenderer(options) {
function render(vnode, container) {
patch(null, vnode, container, null);
}
// n1,n2代表新旧subTree
function patch(n1, n2, container, parentComponent) {
// 需要判断vnode是组件还是element
const { type, shapeFlag } = n2;
switch (type) {
// Fragment只渲染children
case Fragment:
processFragment(n2, container, parentComponent);
break;
case Text:
processText(n2, container);
break;
default:
if (shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.ELEMENT) {
processElement(n1, n2, container, parentComponent);
} else if (shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.STATEFUL_COMPONENT) {
// 处理组件
processComponent(n2, container, parentComponent);
}
break;
}
}
function processElement(n1, n2, container, parentComponent) {
if (!n1) {
// 组件初始化
mountElement(n2, container, parentComponent);
} else {
// 更新组件视图
patchElement(n1, n2, container);
}
}
function patchElement(n1, n2, container) {
console.log("patchElement");
console.log("current", n2);
console.log("prev", n1);
}
...
function mountChildren(vnode, container, parentComponent) {
vnode.children.forEach((v) => {
// 挂载子节点的时候 不会有旧节点
patch(null, v, container, parentComponent);
});
}
...
function setupRenderEffect(instance, initialVNode, container) {
// 当响应式对象发生改变, 触发函数
effect(() => {
if (!instance.isMounted) {
// 首次挂载
const { proxy } = instance;
// 保存subTree
const subTree = (instance.subTree = instance.render.call(proxy));
// 初始化的时候没有旧节点
patch(null, subTree, container, instance);
initialVNode.el = subTree.el;
instance.isMounted = true;
} else {
const { proxy } = instance;
const subTree = instance.render.call(proxy);
const prevSubTree = instance.subTree;
// 获取新旧subTree并更新
instance.subTree = subTree;
patch(prevSubTree, subTree, container, instance);
}
});
}
}
# 更新 element 的 props
# 简介
处理 element 的 props 变化, 首先修改测试用例, 增加对 element 的 props 修改
import { h, ref } from "../../lib/mini-vue.esm.js";
export const App = {
name: "App",
setup() {
const count = ref(0);
const onClick = () => {
count.value++;
};
const props = ref({
foo: "foo",
bar: "bar",
});
const onChangePropsDemo1 = () => {
props.value.foo = "new-foo";
};
const onChangePropsDemo2 = () => {
props.value.foo = undefined;
};
const onChangePropsDemo3 = () => {
props.value = {
foo: "foo",
};
};
return {
count,
onClick,
onChangePropsDemo1,
onChangePropsDemo2,
onChangePropsDemo3,
props,
};
},
render() {
return h(
"div",
{
id: "root",
...this.props,
},
[
h("div", {}, "count:" + this.count),
h(
"button",
{
onClick: this.onClick,
},
"click"
),
h(
"button",
{
onClick: this.onChangePropsDemo1,
},
"changeProps - 值改变了 - 修改"
),
h(
"button",
{
onClick: this.onChangePropsDemo2,
},
"changeProps - 值变成了 undefined - 删除"
),
h(
"button",
{
onClick: this.onChangePropsDemo3,
},
"changeProps - key 在新的里面没有了 - 删除"
),
]
);
},
};
# 代码
基于上一节的代码, 我们把更新视图的代码都放在了 renderer.ts 的 patchElement 函数中, 这里对函数进行扩展.
const EMPTY_OBJ = {};
function patchElement(n1, n2, container) {
console.log("patchElement");
console.log("current", n2);
console.log("prev", n1);
// 获取新旧节点的props
const oldProps = n1.props || EMPTY_OBJ;
const newProps = n2.props || EMPTY_OBJ;
const el = (n2.el = n1.el);
patchProps(el, oldProps, newProps);
}
function patchProps(el, oldProps, newProps) {
if (oldProps !== newProps) {
for (const key in newProps) {
const prevProp = oldProps[key];
const nextProp = newProps[key];
// 更新props值
if (prevProp !== nextProp) {
hostPatchProp(el, key, prevProp, nextProp);
}
}
// 删除旧props多余的属性
if (oldProps !== EMPTY_OBJ) {
for (const key in oldProps) {
if (!(key in newProps)) {
hostPatchProp(el, key, oldProps[key], null);
}
}
}
}
}
同时修改 runtime-dom/index.ts 的 patchProp 函数, 使其支持对 props 的更新
function patchProp(el, key, prevVal, nextVal) {
const isOn = (key: string) => /^on[A-Z]/.test(key);
if (isOn(key)) {
const event = key.slice(2).toLowerCase();
el.addEventListener(event, nextVal);
} else {
if (nextVal === undefined || nextVal === null) {
// 删除属性
el.removeAttribute(key);
} else {
el.setAttribute(key, nextVal);
}
}
}
# 更新 element 的 children
继续补充 patchElement 函数, 在已经支持 props 更新后再增加 children 更新的逻辑代码
export function createRenderer(options) {
// 渲染器新增remove和setElementText函数
const {
createElement: hostCreateElement,
patchProp: hostPatchProp,
insert: hostInsert,
remove: hostRemove,
setElementText: hostSetElementText,
} = options;
function patchElement(n1, n2, container, parentComponent) {
...
patchChildren(n1, n2, el, parentComponent);
}
function patchChildren(n1, n2, container, parentComponent) {
const prevShapeFlag = n1.shapeFlag;
const shapeFlag = n2.shapeFlag;
const c1 = n1.children;
const c2 = n2.children;
if (shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.TEXT_CHILDREN) {
// 更新子节点是 Text 类型
if (prevShapeFlag & ShapeFlags.ARRAY_CHILDREN) {
// 把旧的子节点清空
unmountChildren(c1);
}
if (c1 !== c2) {
// 设置 Text
hostSetElementText(container, c2);
}
} else {
// 更新子节点是 数组
if (prevShapeFlag & ShapeFlags.TEXT_CHILDREN) {
// 清空
hostSetElementText(container, "");
mountChildren(c2, container, parentComponent);
} else {
// diff 算法
}
}
}
function unmountChildren(children) {
for (let i = 0; i < children.length; i++) {
const el = children[i].el;
// remove
hostRemove(el);
}
}
}
同时在 runtime-dom/index.ts 补充默认的 remove 和 setElementText 函数
function remove(child) {
const parent = child.parentNode;
if (parent) {
parent.removeChild(child);
}
}
function setElementText(el, text) {
el.textContent = text;
}
你可能已经注意到, 当新旧节点的子节点都是数组的时候, 我们需要采用 diff 算法, 这一节里并不打算深入说明, 有关于 diff 算法将会在新的章节里详细讲解
# 更新组件的 props
# 简介
除了对 element 的更新, 我们也需要对组件进行更新
# 代码
和更新 element 类似, 在更新组件的时候从 renderer.ts 的 processComponent 函数入手
function processComponent(n1, n2, container, parentComponent, anchor) {
if (!n1) {
mountComponent(n2, container, parentComponent, anchor);
} else {
updateComponent(n1, n2);
}
}
function mountComponent(initialVNode, container, parentComponent, anchor) {
// 将组件实例存入虚拟节点中
const instance = (initialVNode.component = createComponentInstance(
initialVNode,
parentComponent
));
setupComponent(instance);
setupRenderEffect(instance, initialVNode, container, anchor);
}
function updateComponent(n1, n2) {
const instance = (n2.component = n1.component);
if (shouldUpdateComponent(n1, n2)) {
instance.next = n2;
// 调用setupRenderEffect的effect
instance.update();
} else {
n2.el = n1.el;
instance.vnode = n2;
}
}
// 判断是否需要更新组件 props
function shouldUpdateComponent(prevVNode, nextVNode) {
const { props: prevProps } = prevVNode;
const { props: nextProps } = nextVNode;
for (const key in nextProps) {
if (nextProps[key] !== prevProps[key]) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
function setupRenderEffect(instance, initialVNode, container, anchor) {
// 将effect绑定到组件实例
instance.update = effect(() => {
if (!instance.isMounted) {
const { proxy } = instance;
// 保存subTree
const subTree = (instance.subTree = instance.render.call(proxy));
console.log(subTree);
// vnode-> patch
// vnode-> element-> mountElement
patch(null, subTree, container, instance, anchor);
initialVNode.el = subTree.el;
instance.isMounted = true;
} else {
const { next, vnode } = instance;
// 判断是否有新的虚拟节点
if (next) {
// 将需要更新的新虚拟节点属性注入到当前组件实例并patch进行更新
next.el = vnode.el;
instance.vnode = next;
instance.next = null;
instance.props = next.props;
}
const { proxy } = instance;
const subTree = instance.render.call(proxy);
const prevSubTree = instance.subTree;
// 获取新旧subTree并更新
instance.subTree = subTree;
patch(prevSubTree, subTree, container, instance, anchor);
}
});
}
# 实现 nextTick 功能
# 简介
在上面已经实现了响应式更新组件和 element, 但是当响应式对象被多次修改的时候, 也就意味着 runtime 会多次更新视图, 如下面的测试代码, 其实我们只需要更新一次视图就行, 但是实际上会更新一百次
import { h, ref, getCurrentInstance } from "../../lib/mini-vue.esm.js";
export default {
name: "App",
setup() {
const count = ref(1);
function onClick() {
for (let i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
console.log("update");
count.value = i;
}
}
return {
onClick,
count,
};
},
render() {
const button = h("button", { onClick: this.onClick }, "update");
const p = h("p", {}, "count:" + this.count);
return h("div", {}, [button, p]);
},
};
解决思路是:
- 执行全部同步任务
- 执行一次异步更新视图
这里就会用到一个微任务的概念, 我们在同步的时候, 把所有要更新的 effect 存放在微任务队列中(重复的 effect 只保存一次).
# 代码
回顾前面 effect 的 scheduler 功能, 每当第二次执行 effect.run 的时候, 会去执行 effect 下的 scheduler 而不是 effect 绑定的 function.
所以可以给 runtime-update 的时候增加一个 scheduler 去将要更新的 effect 存入微任务队列中
找到 renderer.ts
import { queueJobs } from "./scheduler";
function setupRenderEffect(instance, initialVNode, container, anchor) {
instance.update = effect(
() => {
...
},
{
scheduler() {
// 注册微任务队列
queueJobs(instance.update);
},
}
);
}
并且创建 scheduler.ts 管理微任务队列
const queue: any[] = [];
let isFlushPending = false;
export function queueJobs(job) {
// 存入微任务
if (!queue.includes(job)) {
queue.push(job);
}
queueFlush();
}
function queueFlush() {
if (isFlushPending) {
return;
}
// 创建一个promise, 异步执行微任务
isFlushPending = true;
nextTick(flushJobs);
}
export function nextTick(fn) {
// 通过Promise.resolve(), 异步执行fn
return fn ? Promise.resolve().then(fn) : Promise.resolve();
}
function flushJobs() {
isFlushPending = false;
let job;
while ((job = queue.shift())) {
job && job();
}
}
这样不管响应式对象更新多少次, 都只会在同步任务结束后通过 Promise.resolve()去执行一次异步刷新, 极大优化了运行效率.
# 使用 nextTick
修改测试代码
import {
h,
ref,
getCurrentInstance,
nextTick,
} from "../../lib/mini-vue.esm.js";
export default {
name: "App",
setup() {
const count = ref(1);
const instance = getCurrentInstance();
function onClick() {
for (let i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
console.log("update");
count.value = i;
}
console.log(instance);
nextTick(() => {
// 此时组件实例已经完成了异步刷新
console.log(instance);
});
// 使用await也可以查看异步更新后的组件实例
// await nextTick()
// console.log(instance)
}
return {
onClick,
count,
};
},
render() {
const button = h("button", { onClick: this.onClick }, "update");
const p = h("p", {}, "count:" + this.count);
return h("div", {}, [button, p]);
},
};
← 三、运行时核心 五、diff 更新算法 →